Understanding Fiscal Policy and Its Global Effects

The world’s economies are intricate webs, constantly reacting to internal and external forces. One of the most significant tools governments use to steer their economies is fiscal policy. It’s a powerful mechanism that can influence everything from job creation and inflation to international trade and global stability. But what exactly is it, and how does it work on a global stage?
Key Takeaways:
- Fiscal policy involves government spending and taxation to influence the economy.
- Governments use fiscal policy to manage economic growth, unemployment, and inflation.
- Fiscal policy decisions in one country can have significant ripple effects on the global economy.
- Different approaches to fiscal policy, such as expansionary or contractionary measures, have varying impacts.
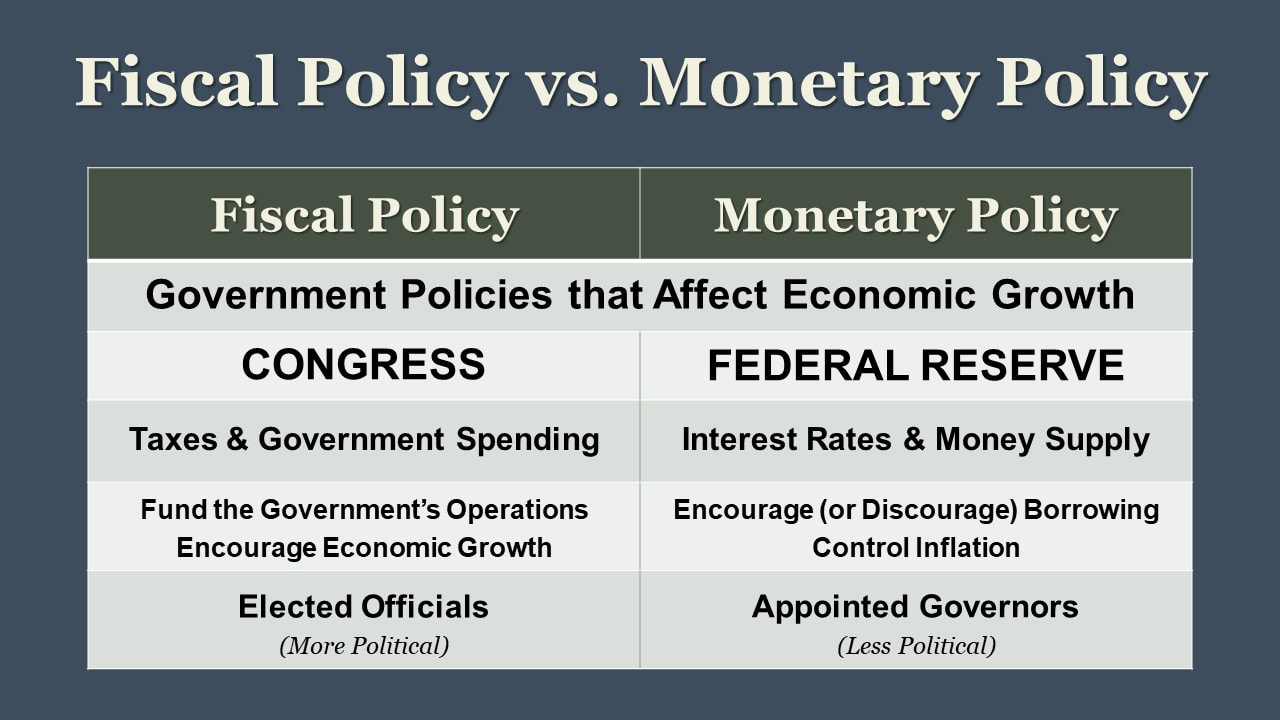
Understanding the Basics of Fiscal Policy
At its core, fiscal policy is the use of government spending and taxation to influence economic conditions. It’s how governments attempt to manage things like economic growth, employment levels, and inflation. When an economy is sluggish, a government might implement expansionary fiscal policy to stimulate activity. This could involve cutting taxes to give people more disposable income or increasing government spending on infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, and public services. The aim is to inject money into the economy, boosting demand and encouraging businesses to invest and hire.
Conversely, when an economy is growing too rapidly and inflation is a concern, a government might employ contractionary fiscal policy. This involves raising taxes or cutting government spending to cool down the economy and prevent prices from rising too quickly. It’s a delicate balancing act, as overly aggressive contractionary measures can stifle growth and lead to a recession. Think of gb (Great Britain) and how its government might adjust spending based on its economic forecasts.
How Fiscal Policy Impacts the Global Economy
Fiscal policy decisions don’t exist in a vacuum. In our interconnected world, what one country does can have significant ripple effects across the globe. For example, if a large economy like the United States or China implements a significant stimulus package, it can increase global demand for goods and services, benefiting exporting nations.
On the other hand, if a country drastically cuts its government spending, it could reduce its demand for imports, negatively impacting its trading partners. Furthermore, fiscal policy decisions can influence exchange rates and capital flows, affecting the competitiveness of businesses and the stability of financial markets worldwide. Consider a scenario where a country increases its interest rates to combat inflation; this can attract foreign investment, strengthening its currency but potentially hurting its export sector.
Examples of Expansionary and Contractionary Fiscal Policy
Let’s look at some practical examples. During the 2008 financial crisis, many countries implemented expansionary fiscal policy measures to combat the recession. The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act in the United States and similar stimulus packages in Europe and Asia aimed to boost demand and prevent a deeper economic downturn. These measures included tax cuts, infrastructure spending, and aid to state and local governments.
Conversely, countries facing high levels of debt or inflation may implement contractionary fiscal policy. For instance, after the Eurozone crisis, several European countries, including Greece and Spain, were forced to implement austerity measures, cutting government spending and raising taxes to reduce their budget deficits. These measures, while necessary to restore fiscal sustainability, often led to slower economic growth and social unrest.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Fiscal Policy
Implementing effective fiscal policy is not without its challenges. One major hurdle is the time lag involved. It can take time for fiscal policy measures to be enacted and even longer for their effects to be felt in the economy. This makes it difficult to fine-tune fiscal policy in response to rapidly changing economic conditions.
Another challenge is political considerations. Fiscal policy decisions often involve trade-offs that are politically unpopular, such as raising taxes or cutting spending on certain programs. This can make it difficult for governments to implement fiscal policy measures that are economically sound but politically challenging. Furthermore, the effectiveness of fiscal policy can depend on a variety of factors, including the state of the economy, the level of government debt, and the credibility of the government.