The agriculture economy is the backbone of many nations, particularly in the developing world. It’s not just about growing food; it’s a complex system involving production, distribution, consumption, and trade, all contributing significantly to economic stability and growth. Without a thriving agriculture economy, nations risk food shortages, economic instability, and widespread poverty.
Key Takeaways:
- Agriculture significantly contributes to global economies through food production, employment, and trade.
- Sustainable farming practices and technological advancements are crucial for long-term economic viability in the agriculture economy.
- Government policies and international trade agreements play a vital role in shaping the agriculture economy and ensuring food security.
- A healthy agriculture economy supports rural communities and contributes to overall economic resilience.
The Foundation: Understanding the Agriculture Economy
The agriculture economy encompasses all economic activities related to agriculture. This includes crop production, livestock farming, forestry, fisheries, and related industries like food processing and agricultural equipment manufacturing. It’s a sector that employs billions worldwide, provides essential food and raw materials, and generates significant revenue through exports. The health of the agriculture economy directly impacts food security, employment rates, and overall economic stability, especially in countries where agriculture forms a large percentage of the gb.
A key aspect of understanding the agriculture economy is recognizing its interconnectedness with other sectors. For example, advancements in agricultural technology, such as precision farming techniques and genetically modified crops, can increase productivity and reduce resource consumption. This, in turn, boosts farm incomes and creates opportunities for related businesses. Similarly, investments in infrastructure, such as irrigation systems and transportation networks, can improve access to markets and reduce post-harvest losses, further strengthening the agriculture economy.
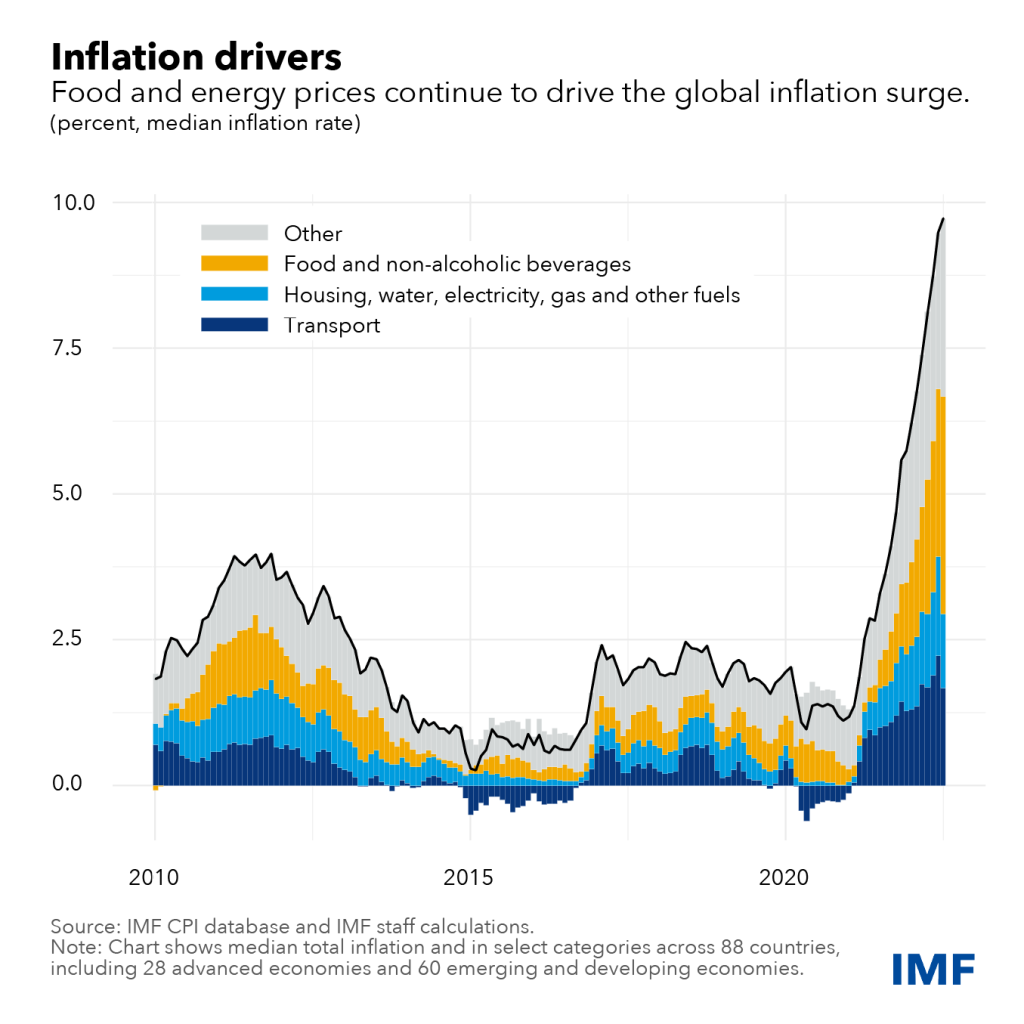
However, the agriculture economy is also susceptible to various challenges, including climate change, volatile market prices, and limited access to credit and technology. These challenges can undermine agricultural productivity and jeopardize the livelihoods of farmers, especially smallholder farmers in developing countries. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that includes promoting sustainable farming practices, investing in research and development, and implementing supportive government policies.
How Agriculture Drives Economic Growth
Agriculture’s impact extends far beyond providing food. A thriving agriculture economy stimulates growth in other sectors, creating a ripple effect throughout the entire economy. For example, increased farm incomes lead to higher consumer spending, which boosts demand for goods and services in other industries. Agriculture also serves as a major source of raw materials for manufacturing, supporting industries such as textiles, food processing, and biofuels.
Furthermore, the agriculture economy plays a crucial role in international trade. Many countries rely on agricultural exports to generate foreign exchange and finance imports of other essential goods and services. A strong agriculture economy allows countries to compete effectively in global markets, attract foreign investment, and improve their overall economic performance. The gb has historically seen the importance of agriculture for trade.
However, realizing the full potential of agriculture as a driver of economic growth requires strategic investments in research and development, infrastructure, and education. These investments can improve agricultural productivity, reduce post-harvest losses, and enhance the competitiveness of agricultural products in global markets. Additionally, promoting sustainable farming practices can help to protect natural resources and ensure the long-term viability of the agriculture economy.
The Impact of Technology and Innovation on Agriculture
Technological advancements are revolutionizing the agriculture economy, offering opportunities to increase productivity, reduce costs, and improve the sustainability of farming practices. Precision farming techniques, such as GPS-guided tractors and drone-based crop monitoring, allow farmers to optimize inputs and reduce waste. Genetically modified crops can offer resistance to pests and diseases, reducing the need for pesticides and increasing yields.
Furthermore, digital technologies are transforming the way farmers access information, connect with markets, and manage their operations. Mobile apps provide farmers with real-time weather updates, market prices, and agronomic advice. Online platforms connect farmers directly with buyers, reducing transaction costs and improving access to markets.
However, ensuring that all farmers, especially smallholder farmers in developing countries, can benefit from these technological advancements requires addressing issues such as access to credit, infrastructure, and education. Governments and international organizations have a role to play in providing support and training to help farmers adopt new technologies and improve their livelihoods.
Policy and Sustainability in the Agriculture Economy
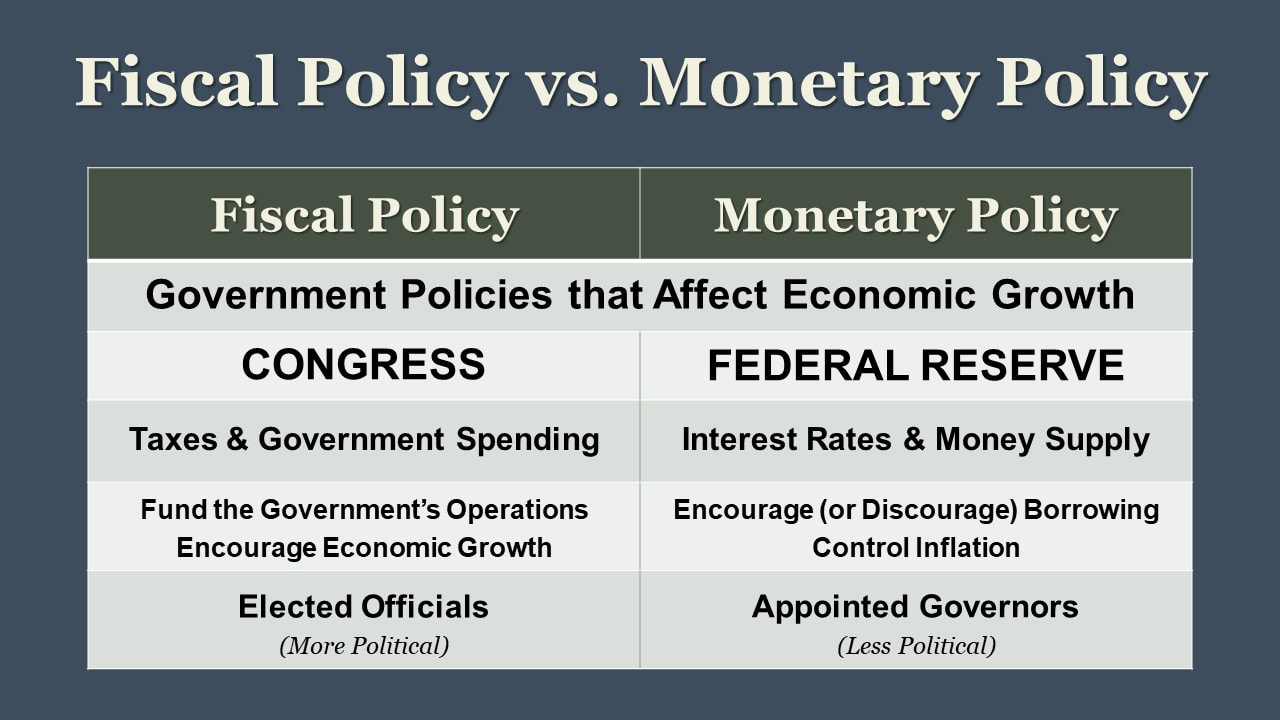
Government policies play a critical role in shaping the agriculture economy. Policies related to trade, subsidies, land use, and environmental regulations can have a profound impact on agricultural productivity, food security, and the sustainability of farming practices. For example, subsidies can provide farmers with financial support, but they can also distort markets and create inefficiencies.
Sustainable farming practices are essential for ensuring the long-term viability of the agriculture economy. These practices include crop rotation, conservation tillage, integrated pest management, and water conservation. Sustainable farming can help to protect natural resources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and improve the resilience of agricultural systems to climate change.
Promoting sustainable farming practices requires a combination of government policies, research and development, and education. Governments can provide incentives for farmers to adopt sustainable practices, such as tax breaks or subsidies. Research and development can help to develop new and innovative sustainable farming technologies. Education can help to raise awareness among farmers about the benefits of sustainable practices.